
|
ASPERA-3: Neutral Particle Imager
|
 |

|
ASPERA-3: Neutral Particle Imager
|
 |
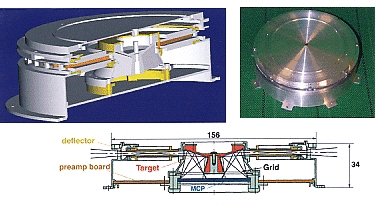 The Neutral Particle Imager head is a replica of the NPI - MCP sensor
developed for the ASPERA - C experiment on the Mars - 96 mission and
successfully flown on the Swedish micro satellite Astrid launched in
1995.
The Neutral Particle Imager head is a replica of the NPI - MCP sensor
developed for the ASPERA - C experiment on the Mars - 96 mission and
successfully flown on the Swedish micro satellite Astrid launched in
1995.
In the NPI the charged particles, electrons and ions, are removed by
the electrostatic deflection system which consists of two disks
separated by a 3 mm gap. The 5 kV potential sweeps away all charged
particles with energies up to 60 keV. Since the integral ENA flux
substantially exceeds the charged particle flux for energies greater
than 60 keV, this rejection energy is sufficient for satisfactory
performance. The disks also collimate the incoming beam in the
elevation angle. Apart from being ON or OFF the deflection system can
be operated in two other modes, alternative mode and sweeping
mode. The deflection system also collimates the beam into 32 sectors.
Neutrals passing through the deflection system hit a 32 sided cone
target with a grazing (20°) angle of incidence. A MCP stack in the Z
configuration detects the particles leaving the target block with 32
anodes. The signal from the MCP gives the direction of the primary
incoming neutral. The MCP operates in ion mode with a negative bias of
-3.0 kV and thus detects (a) sputtered ions of the target material,
(b) ions resulting from stripping of the primary neutrals, and (c)
neutrals reflected from the target surface. In order to improve the
angular resolution and collimate the particles leaving the interaction
surface, 32 separating walls are attached to the target forming a
star-like structure. NPI covers 4p in one instrument scan and produces
an image of the ENA distribution in the form of an azimuth x elevation
matrix. To suppress the UV flux he NPI target uses the same coating as
in the PIPPI and ASPERA-C experiments, namely, DAG 213, a resin -
based graphite dispersion.
| © 2006, Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research, Lindau |
Woch 11-12-2001 |