Convectively Stabilised Models (CSM)
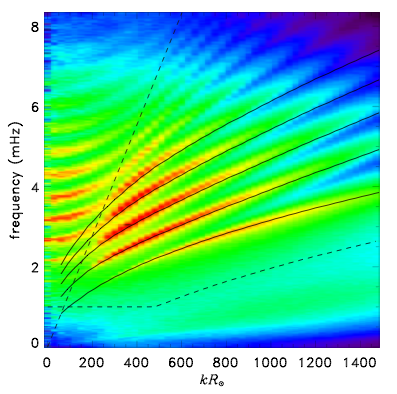 These convectively stabilised models were developed for use in local helioseismology. They have solar-like eigenfunctions and eigenfrequencies. These convectively stabilised models were developed for use in local helioseismology. They have solar-like eigenfunctions and eigenfrequencies.
If you use these models, please contact schunker [at] mps.mpg.de, to obtain the appropriate acknowledgement.
Documentation:
Downloads:
The following are ascii files of the Convectively Stabilised Models (Schunker et al., 2011, in prep).
The columns are
z (Mm) : g (cm/s^2) : dp/dz (g /cm^2 s^2) : rho (g/cm^3) : drho/dz : cs (cm/s)
CSM.dat
CSM_A.dat
CSM_B.dat
Extra information:
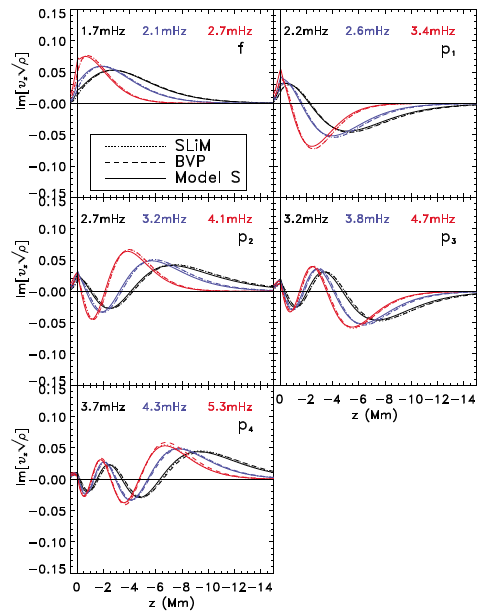 Figure: The z dependence of the real component of Vx sqrt(rho) for a number of eigenmodes of CSM. The corresponding eigenfrequencies are given. The modes have been normalised so that Vz is real at z = 0.2 Mm and have equal integrals. The dashed curve shows the eigenmodes from the BVP solution, the dotted curve shows the eigenmodes from the SLiM simulations and
the solid curve shows the Model S eigenmodes. Each panel corresponds to a different radial order, f, p1 to p4. Figure: The z dependence of the real component of Vx sqrt(rho) for a number of eigenmodes of CSM. The corresponding eigenfrequencies are given. The modes have been normalised so that Vz is real at z = 0.2 Mm and have equal integrals. The dashed curve shows the eigenmodes from the BVP solution, the dotted curve shows the eigenmodes from the SLiM simulations and
the solid curve shows the Model S eigenmodes. Each panel corresponds to a different radial order, f, p1 to p4.
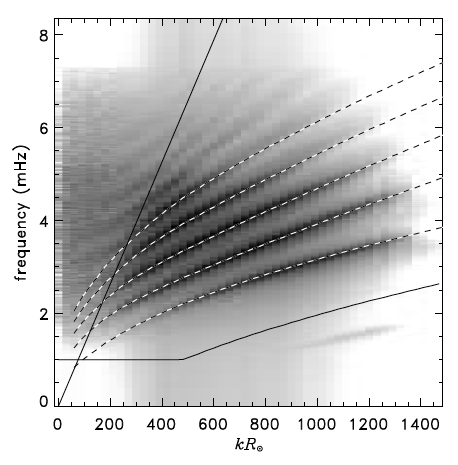 Caption: Azimuthally averaged power spectrum for CSM B using the SPARC code. The Model S eigenfrequencies are overplotted (dashed curves) and the comparable domain is outlined as before. Caption: Azimuthally averaged power spectrum for CSM B using the SPARC code. The Model S eigenfrequencies are overplotted (dashed curves) and the comparable domain is outlined as before.
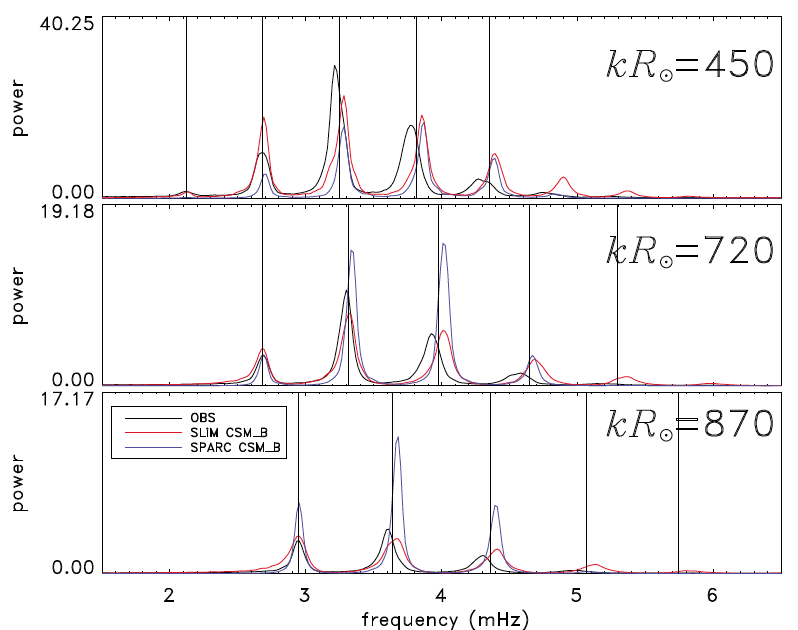 Caption: Cuts through the SPARC power spectrum (blue) and the SLiM power spectrum (red) using CSM A, and the observed power spectrum (black) at different wavenumbers. The Model S eigenfrequencies (vertical lines) are shown for comparison. Caption: Cuts through the SPARC power spectrum (blue) and the SLiM power spectrum (red) using CSM A, and the observed power spectrum (black) at different wavenumbers. The Model S eigenfrequencies (vertical lines) are shown for comparison.
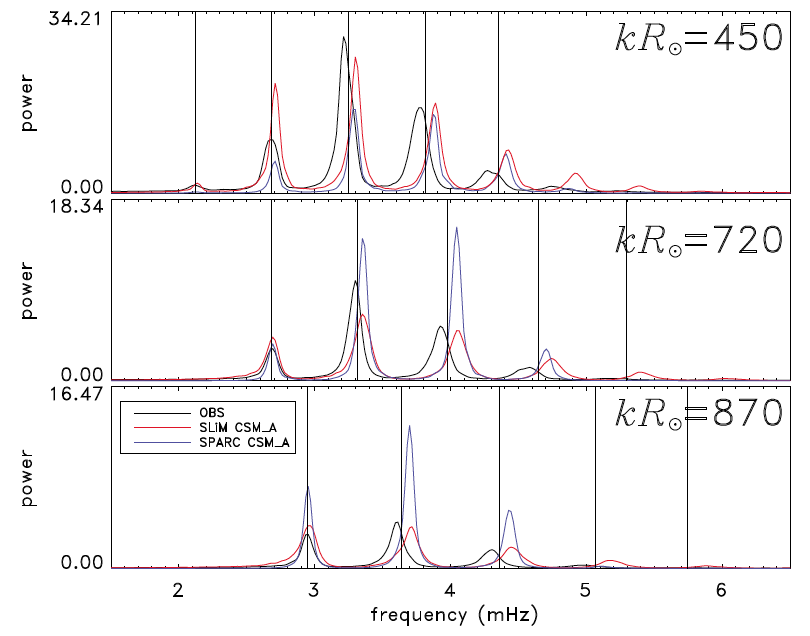 Caption: Cuts through the SPARC power spectrum (blue) and the SLiM power spectrum (red) using CSM B, and the observed power spectrum (black) at different wavenumbers. The Model S eigenfrequencies (vertical lines) are shown for comparison. Caption: Cuts through the SPARC power spectrum (blue) and the SLiM power spectrum (red) using CSM B, and the observed power spectrum (black) at different wavenumbers. The Model S eigenfrequencies (vertical lines) are shown for comparison.
Site Map
This website is best viewed using Firefox, Safari or Internet Explorer browsers.
| 







 These convectively stabilised models were developed for use in local helioseismology. They have solar-like eigenfunctions and eigenfrequencies.
These convectively stabilised models were developed for use in local helioseismology. They have solar-like eigenfunctions and eigenfrequencies. Figure: The z dependence of the real component of Vx sqrt(rho) for a number of eigenmodes of CSM. The corresponding eigenfrequencies are given. The modes have been normalised so that Vz is real at z = 0.2 Mm and have equal integrals. The dashed curve shows the eigenmodes from the BVP solution, the dotted curve shows the eigenmodes from the SLiM simulations and
the solid curve shows the Model S eigenmodes. Each panel corresponds to a different radial order, f, p1 to p4.
Figure: The z dependence of the real component of Vx sqrt(rho) for a number of eigenmodes of CSM. The corresponding eigenfrequencies are given. The modes have been normalised so that Vz is real at z = 0.2 Mm and have equal integrals. The dashed curve shows the eigenmodes from the BVP solution, the dotted curve shows the eigenmodes from the SLiM simulations and
the solid curve shows the Model S eigenmodes. Each panel corresponds to a different radial order, f, p1 to p4. Caption: Azimuthally averaged power spectrum for CSM B using the SPARC code. The Model S eigenfrequencies are overplotted (dashed curves) and the comparable domain is outlined as before.
Caption: Azimuthally averaged power spectrum for CSM B using the SPARC code. The Model S eigenfrequencies are overplotted (dashed curves) and the comparable domain is outlined as before. Caption: Cuts through the SPARC power spectrum (blue) and the SLiM power spectrum (red) using CSM A, and the observed power spectrum (black) at different wavenumbers. The Model S eigenfrequencies (vertical lines) are shown for comparison.
Caption: Cuts through the SPARC power spectrum (blue) and the SLiM power spectrum (red) using CSM A, and the observed power spectrum (black) at different wavenumbers. The Model S eigenfrequencies (vertical lines) are shown for comparison. Caption: Cuts through the SPARC power spectrum (blue) and the SLiM power spectrum (red) using CSM B, and the observed power spectrum (black) at different wavenumbers. The Model S eigenfrequencies (vertical lines) are shown for comparison.
Caption: Cuts through the SPARC power spectrum (blue) and the SLiM power spectrum (red) using CSM B, and the observed power spectrum (black) at different wavenumbers. The Model S eigenfrequencies (vertical lines) are shown for comparison.