
|
Interball ASPI experiment
|
 |

|
Interball ASPI experiment
|
 |
PI's of instruments belonging to the INTERBALL-ASPI Wave-Consortium:
E.Amata, J.Blecki, J.Büchner, J.Juchniewicz, S. Klimov, S.Romanov, J.Rustenbach.
Participating Institutions:
Department of Automatic Control and Systems Engineering, Sheffield
University, Sheffield, UK
Institute of Metrology, St.Peterburg, Russia
Institute of Physics of Atmosphere, Academy of Sciences of Czech Republic,
Praha, Czechia
Interplanetary Space Physics Institute, CNR, Frascati, Italy
Max-Planck-Institut fuer Aeronomie, Katlenburg-Lindau, Germany
Max-Planck-Institut fuer extraterrestrische Physik, Aussenstelle Berlin,
Germany
Space Research Center, Polish Academy of Sciences, Warsaw, Poland
Laboratory of Physics and Chemistry of the Environment, CNRS, Orleans,
France
Sussex Space Centre, Falmer, UK
Space Science Department, ESA, Noordwijk, The Netherlands
Special Design Division, Ukrainian Academy of Sciences, Lviv, Ukraine
Space Research Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russia
Over the years of space research magnetic and electric fields as well
as plasma waves were shown to play a significant role in various space
plasma processes. At the bow shock wave they provide the necessary
dissipation and the observed particle acceleration, at the
magnetopause they allow the transfer of energy from the solar wind
into the magnetosphere, they seem to provide the dissipation in
reconnection regions etc. Also, plasma waves are a very sensitive
indicator of a lack of thermal equilibrium in space plasmas. Features
of the particle distribution function which may be of a small
amplitude, localized in phase space or have a short lifetime, can
produce strong plasma waves. One example is the, produced by electron
beams at the bow shock of the Earth. These beams are rarely identified
in the particle data. The temporal resolution of plasma wave
measurements is about the inverse of the frequency of the wave -
i.e. usually much higher than particle sensors allow. Suitable wave
and field receivers as well as onboard data processing systems allow
time resolutions of a few milliseconds. This is an orders of
magnitude higher resolution as compared to typical plasma and particle
instruments, which is an important step forward in studying boundaries
and other small scale structures. As an example we show the magnetic
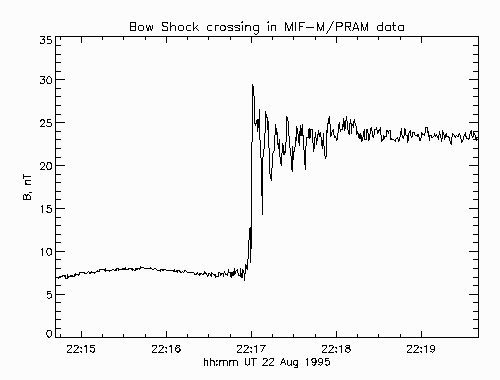
field variation of the INTERBALL-1 bow shock crossing August 22, 1995.
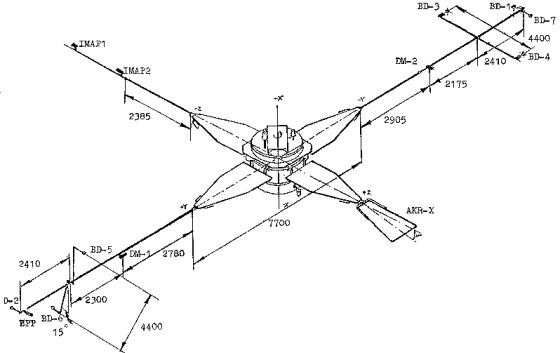
To provide high sensitivity of the electric field, magnetic field and plasma currents measurements a special program of magnetic, electric cleanliness and electromagnetic compatibility measures was implemented basing on the experience of the previous experiments. Unique configuration of the spacecraft with the spin axis pointing to the Sun ensures identical shadowing of electric field sensors. The location of the ASPI sensors on INTERBALL-1 is shown below.
The first three months of the Interball-tail operation in orbit were used by the ASPI teams mainly for estimates of stability of measured parameters and effective sensitivity. The following characteristics of the operating ASPI sensors were obtained.
| Instrument / sensor | Parameter | Frequency range | Measurement range / discretization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic field measurements | |||
| MIF-M/BPP | DC vector | 0-2 Hz | 300/0.29 nT |
| AC vector | 2-25 Hz | 30/0.005 nT | |
| MIF-M/BPP | AC 1 component | 1-40000 Hz | 0.0004 nT at 100 Hz(*) |
| FGM-I/DM1-3 | DC vector | 0-35 Hz | 128/1 nT |
| Electric field measurements | |||
| OPERA/BD1-6 | DC vector | 0-3 Hz | 115/0.9 mV/m (Ey) |
| 570/5 mV/m (Ex,Ez) | |||
| OPERA/BD1-6 | AC vector | 0.1-25 Hz | 115/0.9 mV/m |
| Plasma current measurements | |||
| FGM-I/DM1-3 | AC 1 component | 0.1-40000 Hz | 10^-15 A/cm2/sqrt(Hz)(*) |
| BD-7/C2-X | AC 2 component | 0.1-40000 Hz | 10^-15 A/cm2/sqrt(Hz)(*) |
(*) - sensitivity
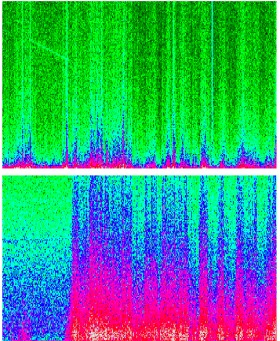 Magnetic field colour spectrogram (MIF-M) in the 0.5-32 Hz frequency
range (bottom panel) displays strong ULF/ELF turbulence in the magnetosheath
(right side) with the intensity and frequency span enlargement. Electric
field colour spectrogram (OPERA) in 0.5-32 Hz band (top panel) shows: (a)
wave bursts at the magnetopause and in the magnetosheath (b) electrostatic
ELF emission inside magnetosphere (left side). Colour bar at the bottom
panel right side shows the color coding of logarithmic wave amplitude.
Magnetic field colour spectrogram (MIF-M) in the 0.5-32 Hz frequency
range (bottom panel) displays strong ULF/ELF turbulence in the magnetosheath
(right side) with the intensity and frequency span enlargement. Electric
field colour spectrogram (OPERA) in 0.5-32 Hz band (top panel) shows: (a)
wave bursts at the magnetopause and in the magnetosheath (b) electrostatic
ELF emission inside magnetosphere (left side). Colour bar at the bottom
panel right side shows the color coding of logarithmic wave amplitude.
Measurements by three-axial fluxgate magnetometers in the MIF-M and FGM-I instruments of ASPI combined with ones from two fluxgates of FM-3I provide a unique possibility to estimate and monitor DC magnetic interferences of the spacecraft.
Klimov,S., S.Romanov, E.Amata, J.Blecki, J.Büchner, J.Juchniewicz, J.Rustenbach, P.Triska, L.J.C.Woolliscroft, S. Savin, Yu. Afanas'ev, U.de Angelis, U.Auster, G.Bellucci, F.Farnik, V.Formisano, P.Gough, R.Grard, V. Korepanov, H.Lehmann, B.Nikutowski, M.Nozdrachev, S.Orsini, M.Parrot, A.Petrukovich, J.L.Rauch, A.Skalsky, J.Slominski, J.G.Trotignon, J.Vojta and R.Wronowski, ASPI experiment: Measurements of fields and waves onboard the INTERBALL-TAIL mission, in INTERBALL - Mission and Payload , CNES-IKI-RSA, p.120-152, 1995.
| © 2006, Max-Planck-Institut für Sonnensystemforschung, Lindau |
J. Buechner 10-12-2001 |