
|
HRSC: High/Super Resolution Stereo Imager
|
 |

|
HRSC: High/Super Resolution Stereo Imager
|
 |

Mars Express is the name of the 2003 ESA mission to Mars. It consists of an orbiter and a small lander, Beagle-2. One of the primary instruments on the orbiter will be the High/Super Resolution Stereo Imager (HRSC).
| Science objectives of HRSC | |
| HRSC instrument description | |
|
MPS involvement contact: Markiewicz |
|
| Related links | |
|
Mars-Express publications by MPS members
|
|
| Group Homepage |
The scientific objectives of the HRSC as formulated by 36 scientists from 7 different countries are:
The HRSC will take images of the surface and atmosphere of Mars in full colour, 3D and at high resolution. Its greatest strength, however, is its unprecedented pointing accuracy, which it achieves by combining images at two different resolutions. This makes it particularly useful for, among other things, assessing potential landing sites for future missions to Mars. The camera, which weighs 21.2 kg will take 3D colour pictures of the Martian surface and of atmospheric phenomena, such as cloud cover and dust storms, at a resolution of 10-30 m. At the same time, a super resolution channel will allow it to home in on selected sites of particular interest for imaging down to 2 m/pixel resolution. Although cameras on other spacecraft have imaged small areas at high resolution, or large areas at low resolution, they have never before combined the two and hence have been unable to determine the location of high resolution images to better than a few kilometres. The HRSC's images will be in 3D and full colour. The 3D imaging will provide a measurement of the height of features within an image relative to each other. The vertical resolution will be similar to the horizontal resolution.
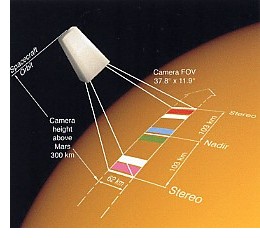
The camera has ten channels, each consisting of a CCD (charge coupled device). One will be the super resolution channel and the other nine will record the same image almost simultaneously at the lower resolution. Four of these channels will record the image at different wavelengths (colours), and five will view it from different angles to provide the 3D effect.
When the camera is 300 km above the surface, its footprint will be 62 km by 206 km. The diagram to the right shows the CCD lines except for the super resolution channel. The five white lines are used to provide the stereo effect.
MPS has no hardware participation in HRSC. We have have however, the leading role within the HRSC team, in the Martian atmospheric science to be done with this instrument. Some of the topics which interest us are:
![]() Institute of Space Sensor Technology and Planetary Exploration
at the DLR, in Berlin
Institute of Space Sensor Technology and Planetary Exploration
at the DLR, in Berlin
| © 2006, Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research, Lindau |
Markiewicz 20-02-2002 |