The following systems are referred to the true Earth equator or ecliptic of date, that is
corrections for nutation and precession should be applied in transformations.
We also give the bracket notation ![]() used by Hapgood (1992) (see Appendix).
used by Hapgood (1992) (see Appendix).
| XY-plane: | True Earth equator of date. |
| +X-axis: | Intersection of Greenwich meridian and Earth equator. |
| Angles: | Geographic latitude and longitude (increasing westward) right handed, |
| in the sense of a planetographic system (see section 4.3). | |
| Transform: |
|
| where the |
| XY-plane: | Earth mean ecliptic of date. |
| +X-axis: | vector Earth-Sun of date. |
| Transform: |
|
| and subtraction of solar position vector if necessary. | |
| Also
|
| +Z-axis: | projection of northern dipole axis on |
| +X-axis: | vector Earth-Sun of date. |
| Transform: |
|
| is the Earth dipole vector in GSE-coordinates. | |
| This can be calculated
from the geographic position |
|
|
|
| +Z-axis: | Normal vector to Earth Magnetopause. |
| +Y-axis: | cross-product of +Z-axis and GSM-Z-axis. |
The normal vector may be determined by a model or by minimum-variance analysis of data.
| +Z-axis: | Northern Earth dipole axis of date. |
| +Y-axis: | cross-product of +Z-axis and Earth-Sun vector of date. |
| Transform: |
|
| where
|
The longitude of this system is also called magnetic local time (MLT)
increasing eastwards from the anti-solar (![]() ) to the solar (
) to the solar (![]() ) direction.
) direction.
| +Z-axis: | Northern Earth dipole axis of date. |
| +Y-axis: | cross-product of Geographic North Pole of date and +Z-axis. |
| Transform: |
|
| where |
Geomagnetic latitude ![]() and longitude
and longitude ![]() (increasing eastward) refer to this system.
(increasing eastward) refer to this system.
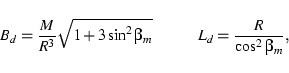 |
(23) |