


Next: Numerical Example
Up: Appendix
Previous: Velocity Transformations
Light Aberration
For physical effects which depend not on the geometric relative position
of two objects  but on the apparent position of
but on the apparent position of 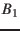 relative
to
relative
to  one has to take light travel into account.
The relativistic deflection of light by the Sun is only
larger than
one has to take light travel into account.
The relativistic deflection of light by the Sun is only
larger than 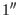 for angular distances from the Sun of less
then
for angular distances from the Sun of less
then  (see [S. Table 3.26.1]) and may be neglected for our purposes.
The change in position during the light travel time
(for example
(see [S. Table 3.26.1]) and may be neglected for our purposes.
The change in position during the light travel time
(for example 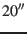 between Sun and Earth)
can be calculated by iteration by determining the geometric
position at time
between Sun and Earth)
can be calculated by iteration by determining the geometric
position at time
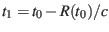 where
where  is the distance between
is the distance between
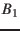 and
and  at
at 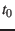 and
and 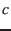 is the speed of light [S. 3.314-315].
The light aberration is caused by the relative speeds of the observer
is the speed of light [S. 3.314-315].
The light aberration is caused by the relative speeds of the observer 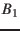 to the
light coming from object
to the
light coming from object  and the aberrated position
of
and the aberrated position
of  moving with relative speed
moving with relative speed 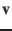 can be calculated
by
can be calculated
by
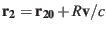 [S. 3.317].
[S. 3.317].
Markus Fraenz
2017-03-13