|
Rio-Imager
Investigation of particle precipitation dynamics in the ionosphere
A new riometer imager experiment with a spatial resolution, exceeding that
of current systems by an order of magnitude, is under construction in
Northern Scandinavia near Tromso. With the Rio-Imager we obtain simultaneous
measurements of ionospheric absorption over a large field of view
(90 000 km^2) with good spatial and temporal resolution. Observations of
the spatial variations of absorption and the dynamics will allow a detail
in the analysis of particle precipitation, which can not at present be
obtained with any other technique.
Science objectives
In studying the Earth's plasma environment it is clear that in situ
measurements are of importance in providing direct information on the
local conditions. In situ measurements are even relevant to 'local'
physics. But no matter how detailed measurements are made on board a
spacecraft or rocket, there are still essential parameters these
measurements cannot determine: the spatial extend over which the
conditions are as in the local region, i.e. spatial variations and
gradients are not determined, nor can the time variations of these
spatial patterns be measured. These are areas where ground based
experiments can complement and extend space observations. Spacecraft
or rockets above the ionosphere can measure the characteristics of
energetic particle fluxes precipitating into the ionosphere in great
detail. The spatial pattern and the dynamics of the precipitation can,
however, only be determined by an instrument fixed on the ground such
as an imaging riometer.
![[Antenna Image]](/images/projekte/rio-imager/antenna.gif)
Riometers using antennas with narrow antenna beams have been widely
used to study acceleration, propagation, and precipitation of
energetic charged particles into the Earth's ionosphere.
A new riometer imager experiment with a spatial resolution, exceeding
that of current systems by an order of magnitude, is under
construction in Northern Scandinavia near Tromso. This site in the
auroral zone is chosen because it allows joint observations with many
other experiments: STARE (=Scandinavian Twin Auroral Radar Experiment)
measures horizontal electron flows in the ionospheric E region over a
large area (400*400 km) with good spatial resolution (20*20 km);
EISCAT provides detailed plasma physical parameters in an area over
Tromso (for example vertical variations of electron density and
electron collision frequency). Also optical measurements (DASI),
neutral wind observations, and HF radar experiments are available over
northern Scandinavia. Rockets launched from Andoya - and Kiruna Rocket
Ranges have trajectories passing inside the field of view of the
riometer imager. Several spacecraft missions will provide further
opportunities for joint research: POLAR, WIND, INTERBALL, GEOTAIL,
CLUSTER, SOHO.
The new riometer imager experiment is based on the principles of a
Mill's Cros. The antenna array consist of two perpendicular rows of
antennas, each row containing 32 antenna. Each row is connected to an
32-element Butler Matrix. In this way 32 dish-like fan shaped antenna
lobes are formed located symmetrically around zenith and with the fans
perpendicular to the vertical plane containing the row of
antennas. The fans associated with the two rows are therefore
perpendicular to each other. The signal is received in each of the
outputs from the two Butler Matrices. Considering a fan from each
Butler Matrix (fan-"i" and fan-"j"), the common solid angle of these
define a direction, a narrow beam, and the received signals have in
common the signal from this direction. Cross correlating the signals
from the two dish-like beams yield a measure, the cross-correlation
(Iij), of the signal intensity in the common direction. In this way
directional intensities can be obtained in a number of direction that
equals the square of the number of antennas in one arm of the Mill's
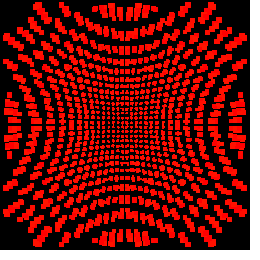
Cross (322 = 1024). The area of intersection of each antenna beam with
the ionosphere is shown in Figure 2 to
illustrate the spatial resolution and coverage of the Rio-Imager
experiment.
![[Top]](/images/icons/top.gif)
Station parameters
Coordinates : 69.7N, 19.23E
Frequency : 38.2 MHz
Number of antennas : 64
Half power beam width : 3.6 degrees
Resolution in 90 km altitude : 6 km
Field of view : 300x300 km
Time resolution : 1 s
![[Top]](/images/icons/top.gif)
Observational parameters
With the Rio-Imager we obtain simultaneous measurements of ionospheric
absorption over a large field of view with good spatial and temporal
resolution. Observations of the spatial variations of absorption and
the dynamics will allow a detail in the analysis of particle
precipitation, which can not at present be obtained with any other
technique.
![[Top]](/images/icons/top.gif)
Related links
The Rio-Imager experiment is a joint project between Germany and United
Kingdom.
 Max-Planck-Institut für
Sonnensystemforschung
(MPS), Dr. E. Nielsen,
Germany
Max-Planck-Institut für
Sonnensystemforschung
(MPS), Dr. E. Nielsen,
Germany
 Lancaster University, Department of Communication
, Dr. F. Honary, UK
Lancaster University, Department of Communication
, Dr. F. Honary, UK
|
